Proxy Servers
How do proxy servers work and what are forward and reverse proxies?
Internet has connected people across the world using social media and audio/video calling features along with providing an overabundance of knowledge and tools. All this comes with an inherent danger of security and privacy breaches. In this guide we will talk about proxies which play a vital role in mitigating these risks. We will cover the following topics in this guide:
Proxy Server
Every web request which is sent from the client to a web server goes through some type of proxy server. A proxy server acts as a gateway between client (you) and the internet and separates end-users from the websites you browse. It replaces the source IP address of the web request with the proxy server's IP address and then forwards it to the web server. The web server is unaware of the client, it only sees the proxy server.
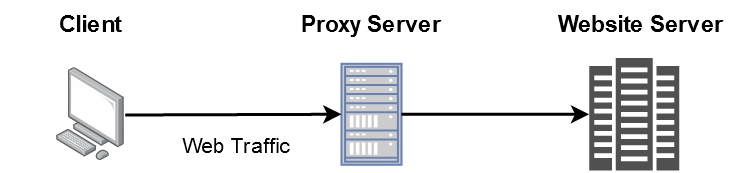
NOTE: This is not an accurate description rather just an illustration.
Proxy servers serve as a single point of control making it easier to enforce security policies. It also provides caching mechanism which stores the requested web pages on the proxy server to improve performance. If the requested web-page is available in cache memory then instead of forwarding the request to the web-server it will send the cached webpage back to the client. This saves big companies thousands of dollars by reducing load on their servers as their website is visited by millions of users every day.
Forward Proxy Server
A forward proxy is generally implemented on the client side and sits in front of multiple clients or client sources. Forward proxy servers are mainly used by companies to manage internet usage of their employees and restrict content. It is also used as a firewall to secure company's network by blocking any request which would pose threat to the companies's network. Proxy servers are also used to bypass geo-restriction and browse content which might be blocked in user's country. It enables users to browse anonymously, as the proxy server masks their details from the website's servers.
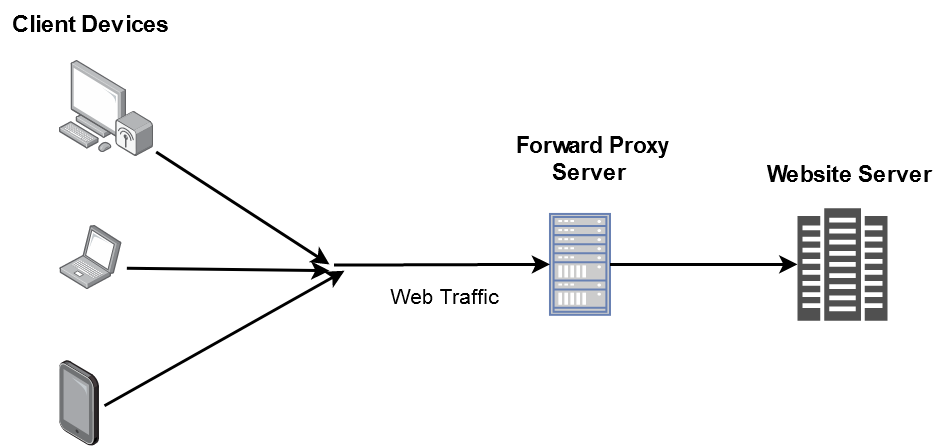
NOTE: This is not an accurate description rather just an illustration
Reverse Proxy Server
Reverse proxy servers are implemented on the server side instead of the client side. It sits in front of multiple webservers and manages the incoming requests by forwarding them to the web servers. It provides anonymity for the back-end web servers and not the client. Reverse proxy servers are generally used to perform tasks such as authentication, content caching, and encryption/decryption on behalf of the web server. These tasks would hog CPU cycles on the web server and degrade performance of the website by introducing high amount of delay in loading the webpage. Reverse proxies are also used as load balancers to distribute the incoming traffic efficiently among the web servers but it is not optimized for this task. In essence, reverse proxy server is a gateway to a web-server or group of web-servers.
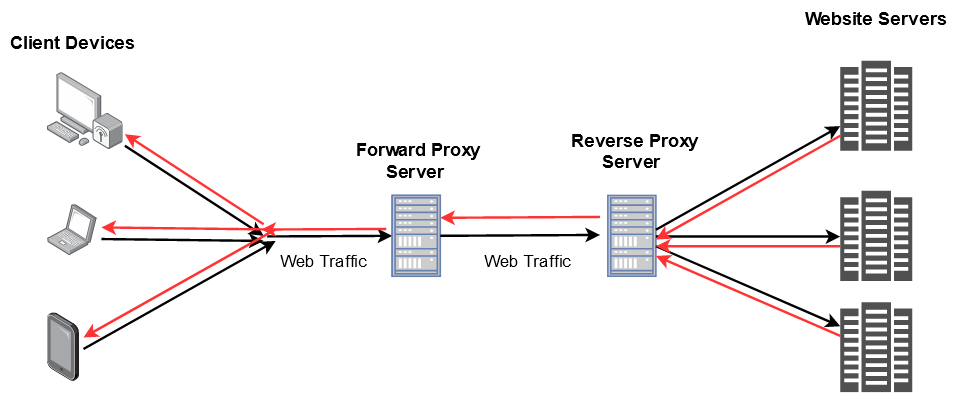
NOTE: This is not an accurate description rather just an illustration. Red lines represent server's response and black lines represent initial request from client(s).
Summary
A proxy server acts as a gateway between client (you) and the internet and separates end-users from the websites you browse. The position of the proxy server on the network determines whether it is a forward or a reverse proxy server. Forward proxy is implemented on the client side and sits in front of multiple clients or client sources and forwards requests to the web server. Reverse proxy servers are implemented on the server side it sits in front of multiple webservers and manages the incoming requests by forwarding them to the web servers.
If all this was too much to take in, I have a simple analogy for you.
At a restaurant the waiter/waitress takes your order and gives it to the kitchen head chef. The head chef then calls out the order and assigns tasks to everyone in the kitchen.
In this analogy:
- You are the client
- Your order is the web request
- Waiter/Waitress is your forward proxy server
- Kitchen head chef is the reverse proxy server
- Other chefs working in the kitchen are the web servers
With that said our guide comes to an end. Thank you for reading and feel free to submit any updates to the guide using the links below.
Open Source
The project is OpenSource, 7th most starred project on GitHub and is visited by hundreds of thousands of developers every month.
A considerable amount of my time is spent doing unpaid community work on things that I hope will help humanity in some way. Your sponsorship helps me continue to produce more open-source and free educational material consumed by hundreds of thousands of developers every month.
Stay Informed
Subscribe yourself to get updates, new guides, videos and roadmaps in your inbox.
Free subscription for updates
Support the project by paying as little as 5$ per month